NIHCM Newsletter / May 2022
Reproductive Health Care
Released: May 11, 2022
Reproductive Health Care
Access to reproductive health services in the U.S. could be further limited if the recently leaked Supreme Court draft decision becomes law and overturns Roe v. Wade. The U.S. already has the highest maternal mortality rate among wealthy countries and experts say pregnancy-related deaths could rise over 20% or more in states where abortion may soon become illegal or seriously limited.
- Unequal Impact: Health professionals and policy analysts say the Supreme Court ruling would disproportionately impact people who already face significant barriers to accessing reproductive health services, including women of color, low-income individuals, and those who live in rural areas.
- Maternal Mortality: Reduced access to reproductive health services could especially impact high-risk pregnancies. The stakes of reduced access to reproductive health care are not even - in DC, Black women account for about half of all births but 90% of all pregnancy-related deaths. Nationwide, Black women are three times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women.
- Supporting Mothers: In addition to the need to improve access to reproductive health services, there is also a need to address gaps in maternal support in the U.S. which is lacking in terms of paid leave, child care, and pay.
Resources & Initiatives
- NIHCM Grantee, USC Annenberg Center for Health Journalism, recently held a webinar discussing "What Comes After Roe v. Wade?"
- Learn more about access to abortion and women’s health care in light of the possible Supreme Court decision in Guttmacher Institute resources.
- This article in Scientific American examines the health and financial impacts of requiring people to carry pregnancies to term.
Cigarettes: Vaping & Menthols
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is banning all menthol cigarettes and flavored cigars, which officials estimate will prevent about half a million U.S. tobacco-linked deaths each year. Additionally, efforts are continuing to curb vaping/e-cigarette use.
- Menthol Ban: Banning menthol cigarettes would have the biggest impact on Black smokers, 85% of whom use menthol products, compared to 29% of White smokers.
- E-cigarettes and Teens: The recent popularity of e-cigarettes complicates efforts to reduce nicotine use among U.S. teens and despite the FDA’s efforts to regulate usage, vaping sales have risen.
Resources & Initiatives
- Learn how Maine, where 18% of adults use cigarettes, has increased funding for smoking cessation programs.
- Learn about the dangers of e-cigarettes from this BlueCross BlueShield of Texas resource.

COVID-19 has become the third biggest killer in the U.S.
COVID-19: Q&A
Q: What is the toll of COVID?
A: Over 1 million people in the U.S. have died from COVID, which has become the third biggest killer behind heart disease and cancer. Nine million close relatives are grieving the loss of spouses, parents, grandparents, siblings, and children to COVID.
Q: Should we be concerned about rising cases?
A: COVID hospitalizations are rising and hotspots are putting pressure on health care systems. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends wearing masks while traveling and some places, such as Chicago, are recommending masks indoors again.
Q: What’s the news on children?
A: As of February, as many as 75% of children have been infected with the virus. The FDA recently laid out a tentative timeline for reviewing vaccine applications from Moderna and Pfizer for children under 5. A top official from the agency said that at least one of the two shots could become available in June and they will not delay one vaccine to wait for the other.
Q: Should I get a second booster?
A: A second booster shot is authorized for immunocompromised people and for anyone age 50 and up. However, there is no consensus on the value of a fourth mRNA vaccine dose and eligible people should consider factors such as local transmission, health risks, and treatment access.
Q: News on boosters and variants?
A: Moderna has redesigned its booster to target two strains of coronavirus, generating a strong immune response and potentially available this fall. Currently, three doses of an mRNA vaccine protect against severe disease or death from omicron and delta variants.
Q: Updates on treatments?
A: The FDA approved the first COVID treatment for children twelve and younger. The Biden Administration announced initiatives to increase the use of antiviral pills to treat COVID, with a particular focus on Pfizer’s Paxlovid.
Q: What about the J&J vaccine?
A: The risk of a rare and life-threatening blood clot syndrome from the Johnson & Johnson (J&J) vaccine has prompted the FDA to impose strict restrictions and only people who would otherwise remain unvaccinated can get the shot.
Hepatitis, Antibiotic Resistance, & Infectious Disease
The CDC is investigating 109 cases of hepatitis in children of unknown origin. In other news, a recent study estimated that in 2019, nearly 1.3 million people died globally from antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, resulting in more deaths annually than HIV or malaria. Antimicrobial drug resistance leads to harder or impossible to cure infections, threatening the ability to treat infectious diseases.
- Hepatitis in Children: Prompted by the recent rise in cases across the U.S., the U.K., Spain, Denmark, Israel, and the Netherlands, the CDC released a nationwide health alert calling for doctors to be on the lookout for children suffering from hepatitis.
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Many public health experts are concerned over the next major health crisis - the overuse of antibiotics, superbugs, and antimicrobial resistance. Gonorrhea could soon become an untreatable infectious disease, as nearly half of all cases are drug-resistant.
- A New Kind of Forecasting: Last month, the CDC launched its Center for Forecasting and Outbreak Analytics to improve the U.S.’ ability to respond to infectious diseases, including decisions about vaccine development and antiviral deployment.
Resources & Initiatives
- Learn more about hepatitis with these resources: the CDC’s Hepatitis A fact sheet, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts’ Hepatitis B guide, and Blue Cross Blue Shield of Oklahoma’s Hepatitis C fact sheet.
- The Washington Post released a hepatitis Q&A as the cases among children in the U.S. continue to increase.
May is Mental Health Awareness Month
Research shows that today, teens are participating less in important activities crucial for healthy development, such as sleep, exercise, and in-person socialization. While the previous public health threats to teens - drunk driving, smoking, and teenage pregnancy - have slowly declined, they have been replaced by a new concern: worsening mental health.
- Mental Health in Teens: Emergency room visits for self-harm increased by 88% between 2001 and 2019 among adolescents between the ages of 10 and 19. The New York Times put together a list of resources to help teens who may be struggling with mental health.
- Reducing Stigma: Anxiety and depression have been on the rise among younger individuals; however, these cases have also aided in reducing the stigma around mental health disorders. Normalizing these conversations allows for more informed and empowered communities.
- Expanding Behavioral Health: In a recent NIHCM webinar, Mental Health Solutions: Improving Care, Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan discussed the collaborative care model, which integrates behavioral health into primary care and reduces barriers to receiving mental health care. Blue Cross Blue Shield of Montana is also expanding access to behavioral health in an effort to address suicide rates across the state.
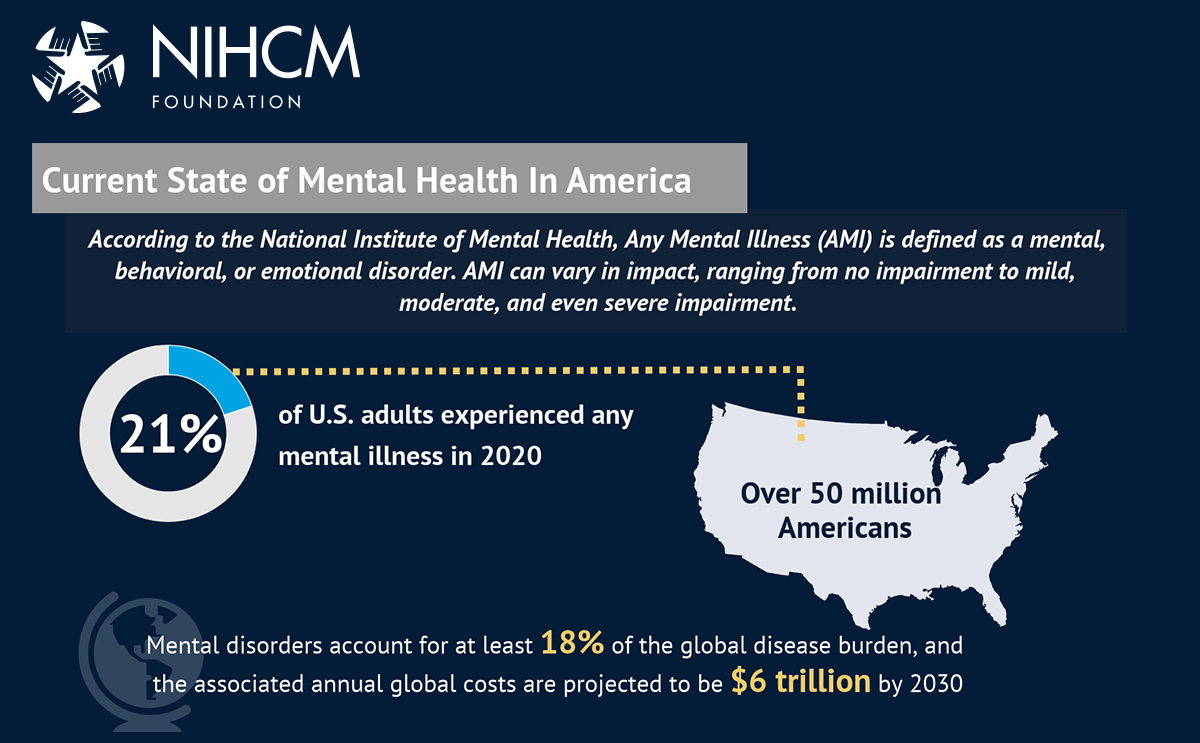
NIHCM’s most recent infographic highlights challenges contributing to the U.S.’ mental health crisis and identifies some steps to improve and strengthen mental health care and the behavioral health industry.
- The Child Mind Institute released resources on how to manage stress and anxiety, as well as avoid passing it to family members.
- Blue Cross Blue Shield of Arizona launched the Foundation for Community and Health Advancement, pledging $5 million to address mental health issues.
- The Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana Foundation partnered with a community organization to expand mental health services in rural areas.
- CNET created a guide on how parents can speak to their children about mental health.

Learn about the winners of the 2022 NIHCM Awards in Journalism and Research! The full body of work honored this year raises awareness of the need to take a new look at many issues that impact our health now and in the future.
See More on:

